PHC piles installation by SIP machine
1. Introduction
The PHC pile installation by SIP machine has been widely adopted in Japan since the 2000s, involves pre-drilling a hole to the design depth with a diameter slightly larger than that of the PHC pile. Once the borehole is prepared, the PHC pile is lowered into it, and cement grout is injected to fill the gap between the borehole wall and the pile shaft, ensuring a strong bond. In this process, an SIP drill rig is employed to drill and simultaneously inject cement grout before placing the PHC pile, stabilizing the borehole and enhancing the load-bearing capacity of piles.
This method is a comprehensive solution that overcomes many limitations of traditional pile installation techniques, such as bored piles, driven piles, and jacked piles. For PHC piles, driving or jacking is often used; however, these methods may be challenging in complex geological conditions, particularly in layers with sand interbedding or when piles must penetrate weathered rock or hard rock layers. Additionally, equipment limitations can make jacking infeasible for large-diameter, deep piles. This method addresses these issues, ensuring technical quality, expediting construction timelines, and optimizing project economics. It is particularly suitable for projects with stringent technical requirements and challenging construction environments.
2. Scope of application
With its compact and safe equipment setup, the pile installation by SIP machine is particularly well-suited for projects with limited construction space, projects built between high-rise structures, or on soft ground. Unlike traditional driven or pressed piling methods, which generate significant vibrations, this method minimizes environmental impact and ensures the safety of surrounding structures. This approach meets stringent technical requirements and is ideal for challenging construction sites where controlling vibrations is essential to protect nearby buildings and infrastructure.
3. Construction sequence
The installation sequence of PHC pile by SIP machine is illustrated in Fig. 1.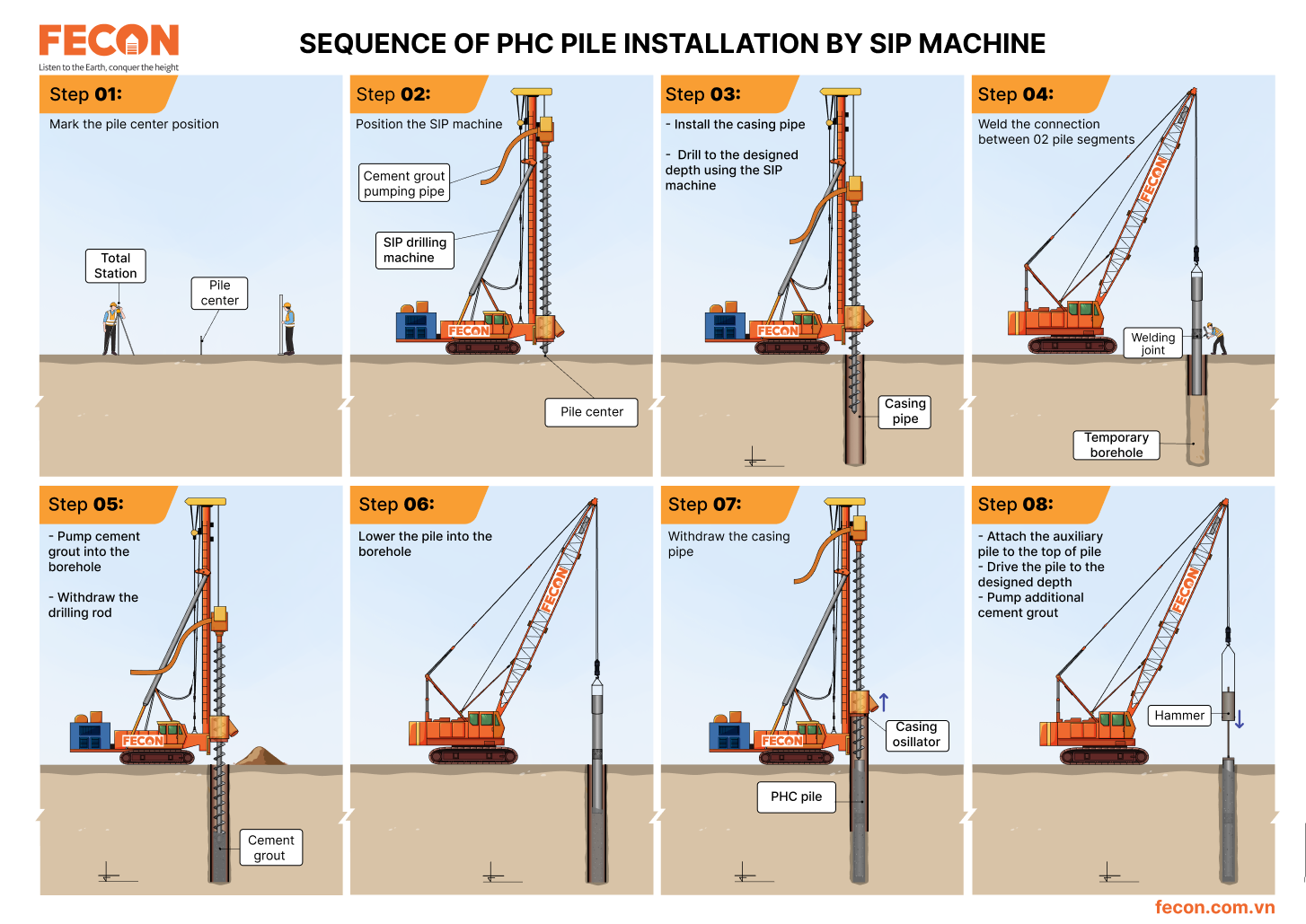
Figure 1. Installation sequence of PHC pile by SIP machine
REFERENCES
[1] Kimura, M. (2014). History of pile foundation technology in Japan and recent pile researches in Kyoto Universioty, a presentation at Hochiminh University of Technology:http://www.dce.hcmut.edu.vn/Resources/public/root/files/02%20Makoto%20Kimura.pdf.
[2] Park, J.B., Kim, J.S. and Chung, H.S. (2003). Bearing capacity characteristics of SIP piles, Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society, 19(1):51-60 (in Korean).
[3] AIJ (2004). Building construction design guidelines, Architectural Institute of Japan (AIJ).
- Foundation and Soil improvement
- Large diameter soil-cement column (RAS) construction method
- Shaft grouted bored pile construction method
- Deep vibro stone columns
- Prefabricated Vertical Drain (PVD) combined with vacuum preloading technology
- PHC piles installation by SIP machine
- Pre-bored pile (BASIC) installation
- Diaphragm wall construction
- Other technologies
- Underground Construction
- Infrastructure Construction
- Building and Plant construction



