Diaphragm wall construction
1. Introduction
The diaphragm wall is a reinforced concrete structure constructed directly on-site, typically used for deep excavations such as foundations or basements. The primary function of a diaphragm wall is to provide support and stability to excavation walls, prevent water seepage, and potentially serve as the basement walls once the construction is complete.
The diaphragm wall construction process begins with the excavation of soil from the ground surface using specialized excavation equipment such as grab buckets or augers. Throughout the excavation process, the excavation walls are stabilized using a bentonite or polymer slurry. Once the excavation is complete, a steel reinforcement cage is lowered into the pit, and concrete is poured through a tremie pipe. As the concrete rises, the bentonite slurry is recovered and can be reused. To ensure a water-tight seal between panels, a water stop is installed at the joints, creating a continuous wall system in the ground. The panels of the diaphragm wall are typically rectangular, with width and depth ranging from 0.5 to 1.8 m and from 12 to 50 m, respectively.
Several critical technical factors must be considered to ensure the quality of diaphragm wall construction:
Formwork and wall guides: The proper use of formwork and wall guides ensures precise shaping and supports efficient concrete pouring.
Bentonite or polymer slurry: Choosing the correct slurry mixture ratio is crucial for stabilizing the excavation walls. The slurry must effectively hold the excavation open while providing support to prevent collapse.
Excavation Integrity: Maintaining the size of the excavation hole is vital to prevent deformation due to environmental influences or external pressure from surrounding soil. Regular cleaning of the excavation pit is essential to maintain its integrity.
Concrete Selection and Pouring: The use of high-quality concrete is essential for durability. Adhering to correct pouring procedures and ensuring skilled labor helps ensure the integrity of the structure.
Waterproofing and Joints: Effective waterproofing solutions must be applied to the diaphragm wall, particularly at the joints between panels, to prevent water ingress.
Safety Measures: Strict safety protocols must be followed, including the careful management of construction equipment and monitoring of construction processes, to safeguard workers and surrounding structures.
2. Scope of application
Diaphragm walls are widely used in various types of construction projects. In high-rise building projects, diaphragm walls are often employed as basement walls and can replace traditional retaining piles with large load-bearing barrette piles, which are more effective than bored piles. Additionally, diaphragm walls are utilized in underground infrastructure projects such as subway stations, underground parking facilities, cut and cover tunnels, and ventilation shafts. In port areas and shipyard facilities, diaphragm walls serve as cutoff walls, water barriers, and retaining walls, while also providing support for deep excavation works.
3. Construction sequence
The construction sequence of diaphragm wall is illustrated in Fig. 1.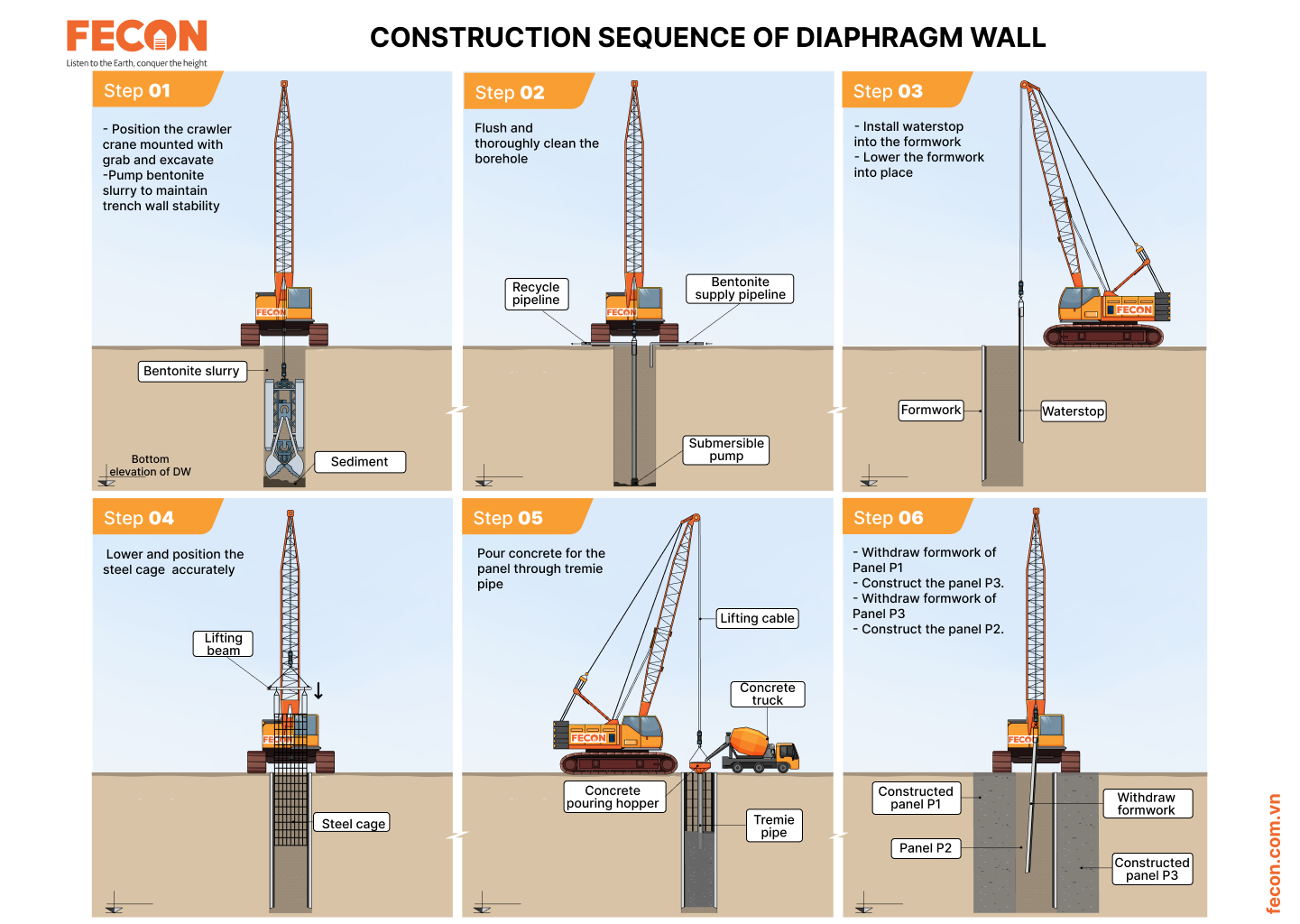
Figure 1. Construction sequence of diaphragm wall
4. Technology video
REFERENCES
[1] C. R. Clayton, R. I. Woods and A. J. Bond, Earth pressure and earth retaining structures - Third edition, 2013.
[2] Engineering News Records, "Soilmec Hydromil shatters slurry-wall records," 2012.
[3] Ban dự án 4, "Biện pháp thi công tường vây," 2017.
[4] Auke Lubach, "Betonite Cavities in diaphragm walls," 2010.
[5] TCVN 9395:2012, "Cọc khoan nhồi - Thi công và nghiệm thu," 2012.
[6] BS EN 1538:2000, "Execution of special geotechnical works - Diaphragm walls," 2000.
[7] Vũ Đức Giang, "Nghiên cứu ứng dụng và quy trình thi công cọc Barrette để đề xuất quy trình nghiệm thu kĩ thuật," 2015.
- Foundation and Soil improvement
- Large diameter soil-cement column (RAS) construction method
- Shaft grouted bored pile construction method
- Deep vibro stone columns
- Prefabricated Vertical Drain (PVD) combined with vacuum preloading technology
- PHC piles installation by SIP machine
- Pre-bored pile (BASIC) installation
- Diaphragm wall construction
- Other technologies
- Underground Construction
- Infrastructure Construction
- Building and Plant construction



