Hot asphalt concrete pavement construction
1. Introduction
Hot asphalt concrete is an important material in the construction of road projects. It is a mixture of crushed stone, sand, and mineral powder, which is heated and mixed with bitumen in a specified ratio. The production of this mixture takes place at specialized mixing plants, and the hot asphalt concrete is then transported to the site and applied using specialized equipment to pave the road surface. There are two main types of hot asphalt concrete: standard hot mix asphalt and polymer-modified hot mix asphalt, each with its own applications and features. Standard hot mix asphalt is suitable for regular road surfaces, providing a stable protective layer, while polymer-modified hot mix asphalt is designed with enhanced features for high-performance transportation projects.
Hot asphalt concrete road surfaces have many advantages, including a dense structure and good load-bearing capacity, which enables the road to withstand high traffic loads without easily wearing out or generating dust. The smooth surface with moderate hardness allows for smooth vehicle movement, reduces noise, and is suitable for mechanized construction. As a result, hot mix asphalt ensures long-lasting road surfaces, contributing to the quality and efficiency of transportation projects.
However, hot asphalt concrete also has some limitations that need to be considered. The dark color of the road surface can make navigation difficult at night. In particular, under high temperatures and prolonged exposure to water, the strength of the road surface tends to decrease, and when the surface is wet, the tire grip also reduces. Additionally, hot mix asphalt can undergo aging due to the effects of time, traffic loads, and climatic conditions, which affects the durability of the road. The construction of hot mix asphalt requires specialized equipment and strict supervision processes, with high technical expertise needed to ensure the quality of the project.2. Scope of application
Hot asphalt concrete is primarily used in the construction of highways, airports, parking lots, industrial buildings, and transportation roads.
3. Construction sequence
The construction process for hot asphalt concrete pavement is illustrated in Fig. 1.
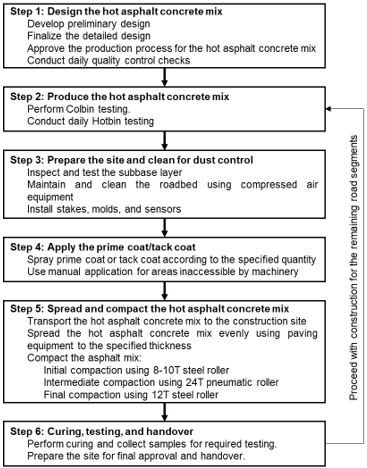 Figure 1. Construction process for hot asphalt concrete pavement
Figure 1. Construction process for hot asphalt concrete pavementREFERENCES
- Tiêu chuẩn ngành "Quy trình công nghệ thi công và nghiệm thu lớp phủ mỏng bê tông nhựa có độ nhám cao" 22 TCN 345 - 06
- Tiêu chuẩn ngành "Quy trình công nghệ thi công và nghiệm thu mặt đường bê tông nhựa" 22 TCN 249 - 98
- Tiêu chuẩn ngành "Quy trình công nghệ thi công và nghiệm thu mặt đường bê tông nhựa sử dụng nhựa đường polyme" 22 TCN 356 - 06
- TCVN 8819-2011: "Mặt đường bê tông nhựa nóng - yêu cầu thi công và nghiệm thu"
- TCVN 8820-2011: "Hỗn hợp bê tông nhựa nóng – Thiết kế theo PP Marshall"
- Quyết định 858/BGTVT về việc áp dụng các tiêu chuẩn hiện hành về BTN cho các đường có lưu lượng cao và chịu tải trọng lớn.
- Bê tông Asphalt – 2008; Tác giả: GS.TS Phạm Duy Hữu – PGS.TS Vũ Đức Chính – TS. Đào Văn Đông – ThS. Nguyễn Thanh Sang
- Foundation and Soil improvement
- Large diameter soil-cement column (RAS) construction method
- Shaft grouted bored pile construction method
- Deep vibro stone columns
- Prefabricated Vertical Drain (PVD) combined with vacuum preloading technology
- PHC piles installation by SIP machine
- Pre-bored pile (BASIC) installation
- Diaphragm wall construction
- Other technologies
- Underground Construction
- Infrastructure Construction
- Building and Plant construction



